Remittances from overseas Indians surged to $29 billion in Q3 of FY 24
Net inward remittances during the quarter was the highest figure since 1991
image for illustrative purpose
One of the most critical aspects of NRI remittances is their role in bolstering India's foreign exchange reserves. In times of economic uncertainties and global financial volatility, these reserves play a pivotal role in ensuring India's macroeconomic stability
India has become the first country to receive over $100 billion in remittances in 2022, according to the United Nations migration agency.
The International Organisation for Migration (IOM) revealed in its World Migration Report 2024 that India’s remittances surged to $111 billion last year, surpassing all other nations.
"India was well above the rest, receiving more than $111 billion, the first country to reach and even surpass the $ 100 billion mark. Mexico was the second-largest remittance recipient in 2022, a position it also held in 2021 after overtaking China, which, historically, was the second-biggest recipient after India,” said the report.
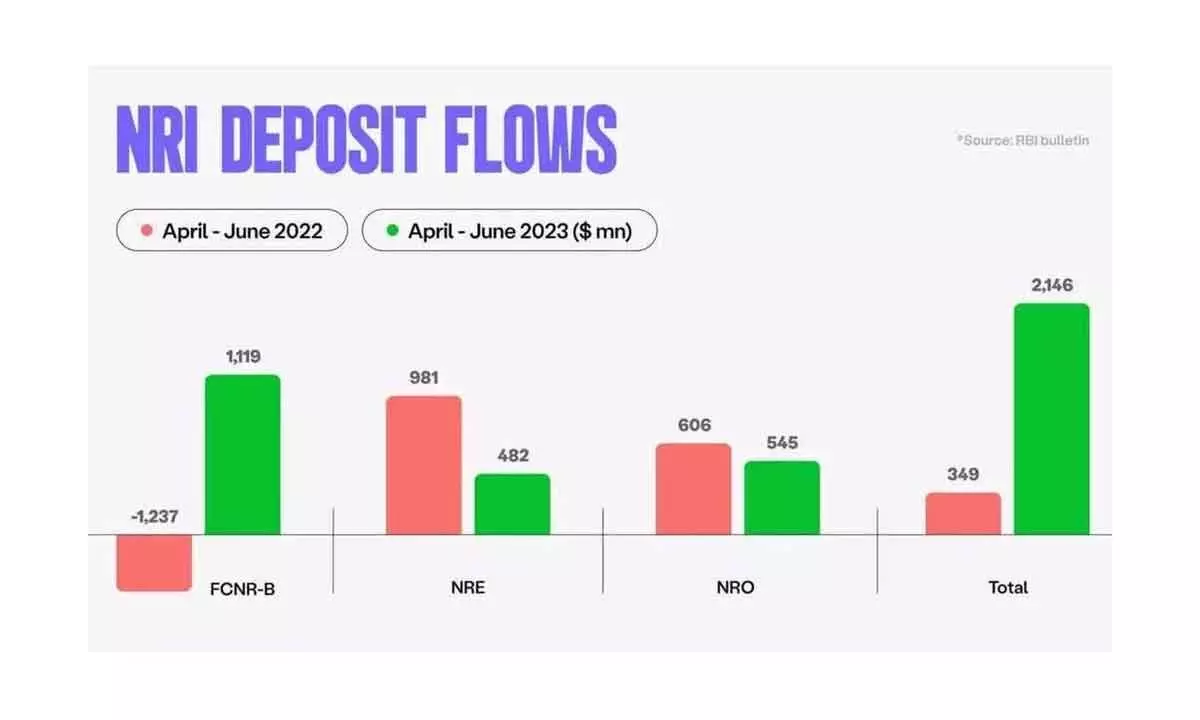
Remittances from overseas Indians surged to $29 billion in Q3 of FY 24, fuelled by the allure of higher returns from FCNR (foreign currency – non-resident) mechanisms as compared to conventional Western bank deposits. Unlike repatriable NRI deposits, remittances constitute steady inflows that play a pivotal role in narrowing India’s current account deficit (CAD), which has been diminishing as a proportion of the country’s GDP.
Preliminary data from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) underscores this trend, revealing a remarkable US$ 29 billion in net inward remittances during the quarter, marking the highest ever recorded figure since 1991. According to a post-Covid survey conducted by the RBI, the United States remains the primary source of remittances, accounting for 23% of the total, while remittances from the Gulf region have witnessed a decline.
Economists attribute this surge in remittances to the robust global economy, particularly in the United States, as well as year-end bonuses disbursed by overseas companies. Remittances hold significant sway over India’s economic landscape, with the nation estimated to have received upwards of US$ 100 billion in inflows in 2023, primarily allocated towards familial support and investment in assets like deposits.
The uptick in remittances, coupled with an upsurge in services exports, has played a pivotal role in curtailing the CAD to 1.2% of GDP in the December quarter. The burgeoning popularity of FCNR deposits, especially amid periods of rupee depreciation, has resulted in substantial inflows, with deposits surpassing three times the levels observed in the preceding year.
In light of the cost disparities across remittance corridors, policymakers are considering measures to broaden the scope of the Money Transfer Service Scheme (MTSS) to facilitate seamless transactions for beneficiaries in India.
Non-resident Indians (NRIs) have long been a cornerstone in strengthening India’s economy, particularly through their remittances. These financial transfers are more than just monetary support to families; they represent a significant contribution to the country's foreign exchange reserves.
One of the most critical aspects of NRI remittances is their role in bolstering India's foreign exchange reserves. Each remittance transaction adds to the country's foreign exchange pool, making it a major source of foreign currency inflow. In times of economic uncertainties and global financial volatility, these reserves play a pivotal role in ensuring India's macroeconomic stability.
NRI remittances are not just numbers in a financial ledger; their impact resonates across the Indian economy. They significantly contribute to the country's Gross Domestic Product (GDP), especially notable during economic slowdowns. This influx of funds boosts the purchasing power of the populace, which in turn stimulates the consumption market, driving both demand and supply.
The increased purchasing power resulting from remittances encourages consumer spending and investment in various sectors of the Indian economy. From real estate to retail, education to healthcare, NRI remittances catalyze a ripple effect that energizes multiple industries. This not only aids in job creation but also promotes overall economic growth of the economy.
In times of economic crisis or global downturns, the consistent flow of remittances has served as a financial cushion for India. It provides a much-needed stable source of foreign currency, helping to offset the impacts of external shocks on the Indian economy.
Despite the significant benefits, managing remittance flows poses certain challenges. Ensuring the efficiency and security of these transactions remains a priority. Furthermore, there lies an opportunity to channel these remittances into more productive investments, contributing to long-term economic development.
The importance of NRI remittances as a source of foreign exchange cannot be overstated. It is testament to the strong ties between the Indian diaspora and their homeland, and their role in shaping the country's economic destiny. As India continues to evolve on the global stage, the contribution of its non-resident citizens will undoubtedly remain a vital part of its growth story.
As of this January, the outstanding NRI deposits stand at $147.73 billion, marking a $823 million rise from December 2023. This growth trend signifies a considerable increase from $136.82 billion recorded in January 2023.

